UAE Mandates Electronic Invoicing: a Complete Shift in Billing and Tax Compliance
The United Arab Emirates is introducing a compulsory electronic invoicing regime, signaling a major transformation in how businesses comply with tax reporting obligations. This initiative represents one of the most far-reaching reforms to the UAE’s fiscal infrastructure in recent years and is intended to modernize UAE bookkeeping practices, improve transparency in tax reporting, and strengthen automated oversight of VAT-related transactions.
Once entrenched, this pioneering framework will redefine the lifecycle of invoices from generation and transmission to authentication and archival across the UAE’s commercial landscape.
Understanding Electronic Invoicing in the UAE
Electronic invoicing, or e-invoicing, entails the creation and exchange of invoices in a rigorously standardized digital format, enabling seamless, automated processing by information systems. Each invoice is meticulously generated, transmitted, verified, received, and stored in a machine-readable configuration. Unlike traditional paper invoices or static PDF documents, e-invoices traverse regulated digital conduits and are systematically validated against statutory mandates.
Under the imminent regulations, paper and PDF invoices will lose their legal standing as evidence for VAT reporting or tax audits. These conventional formats may persist solely for internal documentation, while the electronically registered invoice within the UAE Federal Tax Authority (FTA) ecosystem will hold juridical authority.
Core Pillars of the UAE E-Invoicing System
The UAE’s national e-invoicing architecture imposes exacting technical and operational stipulations, including:
- Utilization of structured invoice formats such as XML or JSON, aligned with UBL and PINT specifications;
- Routing of invoices via officially sanctioned service providers, integrated with the Peppol network and the FTA’s digital infrastructure;
- Automated verification of invoice data with near-instantaneous accuracy;
- Issuance of a unique Invoice Registration Number (IRN), with QR code implementation as mandated;
- Harmonization with corporate ERP systems and accounting platforms.
Gradual Implementation Roadmap
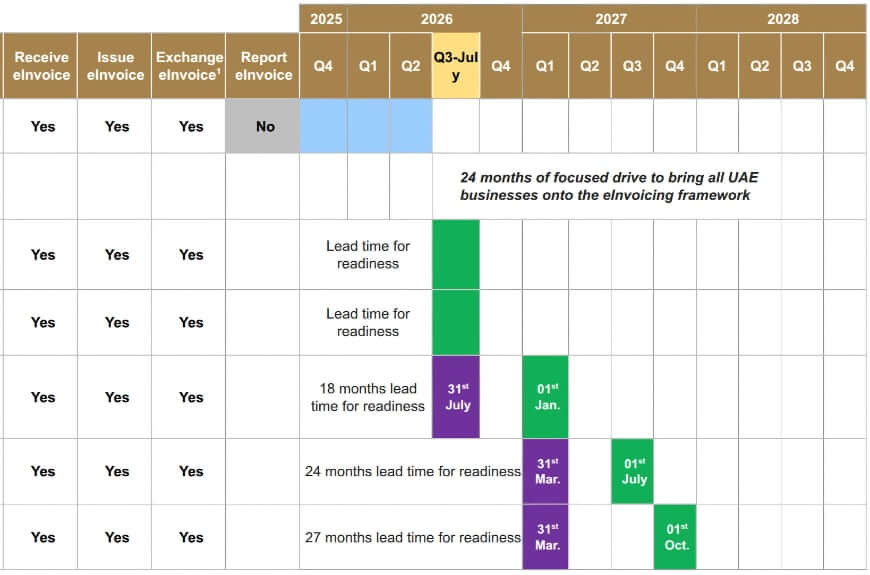
The migration to electronic invoicing will unfold progressively, contingent on organizational scale and type.
Optional Readiness Phase
Commencing July 1, 2026, businesses may voluntarily embrace e-invoicing, enabling trial of technical solutions, refinement of internal workflows, and connectivity with approved service providers.
Stage 1. Large Enterprises
Entities with annual revenues exceeding AED 50 million must appoint an accredited service provider by July 31, 2026. Mandatory deployment of e-invoicing will commence on January 1, 2027.
Stage 2. Small and Medium Enterprises
Businesses with annual turnover below AED 50 million are required to select an approved provider by March 31, 2027. Compulsory e-invoicing for this cohort begins July 1, 2027.
Stage 3. Public Sector Institutions
Federal and local governmental bodies must designate a validated service provider by March 31, 2027, completing e-invoicing adoption by October 1, 2027.
Transactions Falling Within Scope
Initially, the e-invoicing mandate encompasses:
- Business-to-business (B2B) transactions;
- Business-to-government (B2G) exchanges.
Transactions directed at end consumers (B2C) remain excluded at present but could be integrated in subsequent phases.
Practical Value for Businesses
Organizations operating within the UAE should initiate preparatory measures expeditiously, including:
- Audit of current invoicing procedures and VAT compliance frameworks;
- Identification and engagement of a competent accredited service provider;
- Verification that accounting and ERP systems can produce and manage structured e-invoices;
- Training finance and accounting personnel on evolving regulatory and technical imperatives.
Noncompliance may trigger penalties, operational delays, and disruption. Conversely, proactive planning and infrastructure readiness can substantially diminish both implementation costs and compliance exposure.
The mandatory shift to electronic invoicing signals a decisive stride toward a fully digital fiscal ecosystem in the UAE. While the phased rollout extends through 2027, enterprises that act now will secure a seamless, compliant, and streamlined transition into this modernized accounting era.